A domain name is a unique name that identifies a website on the internet. It allows web users to easily remember and navigate to a site instead of having to type a complicated IP address.
Article Highlights
Domain names consist of different levels of names separated by a period or dot. The top level is the suffix like .com or .org. The second level is generally a descriptive name for the site or brand. Additional subdomain levels can be added as well.
So for example, in the domain name www.example.com:
- .com is the top level domain or suffix
- example is the second level domain name
- www. indicates it is the www or web server subdomain
How Domain Names Work
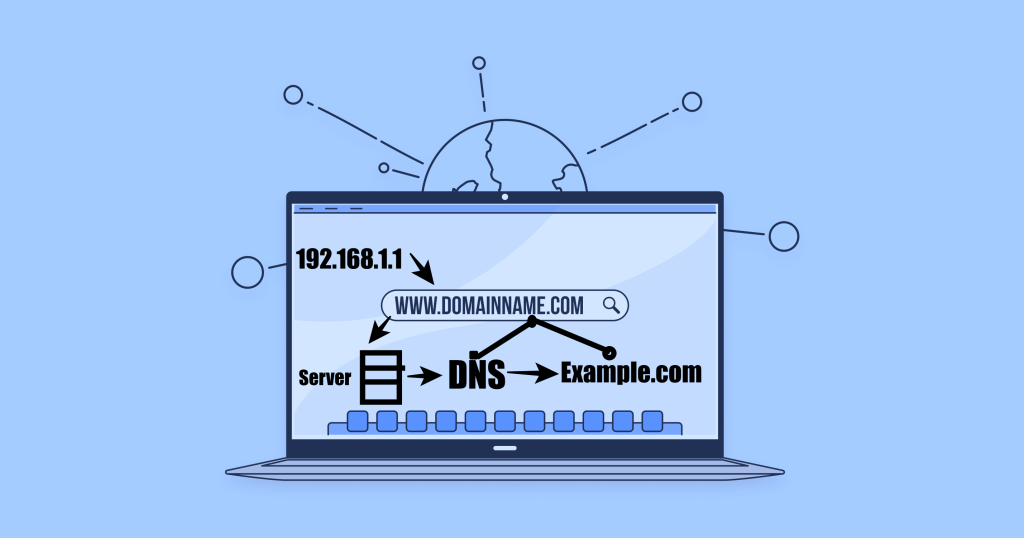
Domain names function by mapping to the unique numerical IP address that identifies each computer connected to the internet. Without domain names, you would have to remember complex IP strings like “192.168.1.1”.
A domain name server (DNS) takes requests and translates domain names into matching IPs so requests are sent to the correct web server.
When you type a domain name URL into a web browser, the browser first pings a DNS to translate the name into an IP. Then a request for the web page or resource can be sent to that IP address. The web server at that IP returns the page to then load the content in the browser.
Main Parts of a Domain Name
The main components in a full domain name from right to left include:
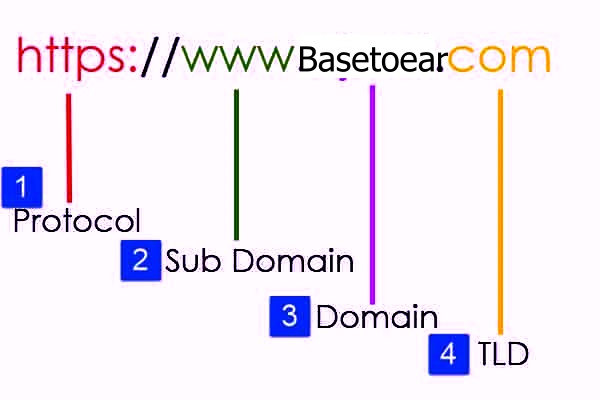
- Top Level Domain (TLD): The suffix like .com, .net, .org, .edu, .gov or country codes.
- Second Level Domain: The custom, descriptive name registered for the site not counting subdomains.
- Subdomains (optional): Prepend subsections of a site like www, mail, secure.
- Hostname: Combined second level plus top level domain.
So for example.com the TLD is .com. The second level or hostname is example.com. Adding a www subdomain gives www.**example.com**.
Having a short, memorable domain name makes it easy for visitors to remember and return to your site. Adding targeted keywords can also help users easily identify what the site is about.
How To Get a Domain Name
There are four main steps to getting your own domain name registered:
- Brainstorm potential domain names
- Use your name, brand, keywords
- Keep it short, simple, memorable
- Check availability of the domain
- Use domain search on registrar sites
- Register for the domain name
- Complete purchase and registration
- Configure DNS records
- Points the domain name to hosting server
Domain names are registered with and managed by domain registrars accredited by ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers). While obtaining hosting space allows a site to actually be built and published online.
Decide if you will self-host or use a web hosting provider. Common affordable hosting providers offer domain registration bundled with hosting services to simplify the process for beginners.
Most Popular Domain Name Suffixes
There are over 1200+ top level domains or extensions now available:
Generic TLDs:
- .com – Most popular, used for commercial sites
- .net – Originally for network infrastructures, now open use
- .org – Intended for non-profit organizations
- .info – Informative sites, also open use generic TLD
Country Code TLDs:
Assigned country codes like:
- .us United States
- .ca Canada
- .uk United Kingdom
Full country code list available at IANA Root Zone Database
New Domain Extensions:
Hundreds of new domain extensions have been introduced in recent years including:
- .blog – sites featuring blogs
- .shop – eCommerce sites
- .app – software applications
- .tech – technology focused sites
See full lists at 101domain TLD Explorer
Choosing the right top level domain helps identify site purpose and build branding. Once a domain expires it becomes available for new registration. Newer TLDs can provide alternatives if common .com names are unavailable.
Most Popular Domain Registrars
Domain registrars are companies accredited by ICANN to sell registration, renewal, and management services for internet domain names.
Criteria for selecting the best domain name registrars include:
- Domain availability
- Competitive pricing
- Renewal costs
- Included private registration
- Management tools
- Customer support
Based on factors like these, some of the overall most popular domain registrars are:
Also read: How to Earn Money with Websites
GoDaddy
The world’s largest domain registrar claiming over 80 million domains registered to date. Offers domain auctions and aftermarket brokerage services.
Pros
- Industry leader ensures reliable services
- Wide range of products bundled as packages
- Highly advertised 99 cent first-year domains
- Excellent domain availability search tools
Cons
- Renewal price hikes
- Upselling and upgrades inflate initial costs
Namecheap
One of the most affordable and reputable budget friendly registrars.
Pros
- Consistently affordable domain pricing
- WhoisGuard privacy protection
- Free services like email forwards
- Excellent customer support response
Cons
- Website upsells can seem pushy
- Less brand popularity than competitors
Bluehost
Popular web hosting provider also offering domain registration services.
Pros
- Domains starting at $2.95 annually
- Includes free private registration
- Easy website builder tools
- Bundles hosting plans with domains
Cons
- Must join hosting to register domains
- Higher renewal costs without bundles
HostGator
Another hosting company providing domain registration and management.
Pros
- Bundles domains with hosting plans
- Easy website builder options
- Excellent uptime and speeds
- Good customer service response
Cons
- Renewal price increases common
- Must purchase hosting for best rates
Evaluating the differences and strengths of top providers helps select the best solution for your specific needs and budget when getting a domain name.
Also read: How to Sign Up for Google AdSense: Monetize Your Website
Conclusion
In summary, a domain name represents the human friendly address for a website that is mapped to the hosting server IP. The most popular domain extensions include .com and country codes. Choosing the right suffix builds branding signals site purpose.
Domain registrars sell annual subscriptions to register available names on a first come basis. Review factors like pricing, included services, renewal terms when selecting domain name providers. Links to top registrars offer options to compare domain registration services.
Also read: How to Find the Best Keywords for Your Next Web Article
Using this overview as a helpful starting guide supports individuals in making informed decisions when embarking on getting their first personally registered domain name and launching a new online presence. Let me know if you have any other questions!
